Seit SQL Server 2005 steht ein eigener Datentyp für XML zur Verfügung.
Convert a Table in XML / Umwandeln einer Tabelle in XML
Die einfachste Methode ist mit Beisatz „FOR XML AUTO“
select * from table1 FOR XML AUTO select * from table1 FOR XML AUTO, ELEMENT
siehe auch hier:
Man kann sich aber auch selbst das XML designen:
SELECT CustomerID as "@CustomerID", CompanyName, Address as "address/street", City as "address/city", Region as "address/region", PostalCode as "address/zip", Country as "address/country", ContactName as "contact/name", ContactTitle as "contact/title", Phone as "contact/phone", Fax as "contact/fax" FROM Customers FOR XML PATH('Customer')
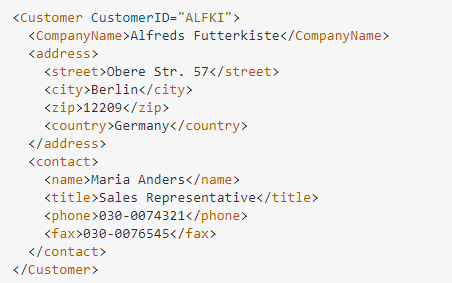
Im Hinblick auf die weitere Verarbeitung in Power BI eignet sich folgende Methode sehr gut:
SELECT * FROM [tbl] AS TM FOR XML AUTO, ELEMENTS, ROOT('Table')
Convert XML in Table / XML in eine Tabelle umwandeln
Der einfachste Anwendungsfall ist, die Rückumwandlung der mit XML Auto erstellten XML Spalte.
Export XML Column Content / Exportieren der XML Spalte
USE [AdventureWorks2012] GO -- Save XML records to a file: DECLARE @fileName VARCHAR(50) DECLARE @sqlStr VARCHAR(1000) DECLARE @sqlCmd VARCHAR(1000) SET @fileName = 'D:\SQL_Queries\PersonAdditionalContactInfo.xml' SET @sqlStr = 'select TOP 1 AdditionalContactInfo from AdventureWorks2012.Person.Person where AdditionalContactInfo IS NOT NULL' SET @sqlCmd = 'bcp "' + @sqlStr + '" queryout ' + @fileName + ' -w -T' EXEC xp_cmdshell @sqlCmd
Wichtig in diesem Zusammenhang sind folgende Dinge:
- Das Select Statement muss in einer Zeile stehen ohne Zeilenumbruch
- Die Datei wird auf dem Server abgelegt, auf dem die Tabelle liegt und nicht auf dem, auf dem das Statement ausgeführt wird.
- Quelle: https://sqlwithmanoj.com/2015/04/13/export-xml-column-data-to-a-file-xml/
weiterführende Informationen:
- General Information:
- Special Topic